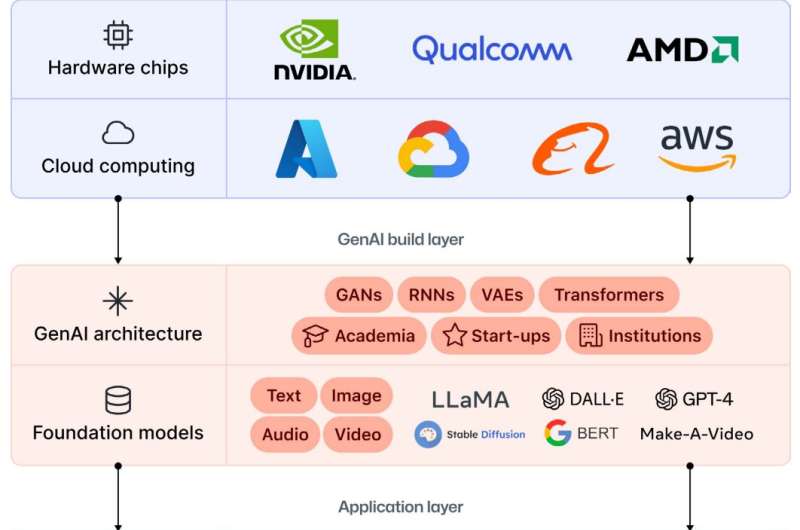
Generative AI Stack. Credit: arXiv (2023). DOI: 10.48550/arxiv.2306.15033
A study of the soaring use of artificial intelligence in software creation says we are in the midst of "a sea change" in program development that will ultimately boost local global gross domestic product by $1.5 trillion by 2030.
In their study, GitHub CEO Thomas Dohmke, Harvard Business School Professor Marco Iansiti and Keystone.AI CEO Greg Richards focused on productivity gained by the widely used GitHub Copilot that, powered by OpenAI Codex, is helping to simplify and speed up the work of software developers.
Copilot, introduced less than a year ago, is an extension for Visual Studio and other developer tools that assist in the creation of programs by offering scripts, natural language suggestions and autocompletion.
Newer versions are integrating the GPT-4 model, introducing enhanced chat and voice support and offering detailed explanation of code as well as bug fixes. With the latest improvements, developers may be able create code without having to touch the keyboard.
Some have compared Copilot to Chat-GPT. Instead of using the power of generative AI technology to produce natural language text, Copilot produces code.
Dohmke said the "symbiotic" relationship between Copilot and GitHub, with 100 million users the world's largest repository for software developers, "has the potential to shape the construction of the world's software for future generations."
Analyzing the activity of nearly a million GitHub developers, Dohmke and his colleagues determined that those using Copilot accepted about 30 percent of its suggestions. Those users reported, and researchers confirmed, increased productivity.
In earlier tests, developers were asked to code an HTTP server in Javascript. Half were permitted access to Copilot while the other half were not. Those utilizing Copilot completed their projects 55 percent faster that those in the control group, Dohmke stated.
In a June 28 tweet, Dohmke addressed concerns of job loss as generative AI is embraced.
"The collision of AI and software development will not decrease the number of software developers, it will lead to more developers that accelerate human progress," he said.
In fact, the authors noted in their report that enormous opportunities will open as a result of this new generation of AI-powered coding tools. They point to Bureau of Labor and Statistics projections of job openings in science and engineering topping 6 million through 2026, along with faster than average growth in IT positions.
"The productivity boost for developers that GitHub Copilot and generative AI tools provide will significantly aid in seizing this opportunity to meet the accelerating software demand," the authors said.
They called for global efforts to expand "education, employment and other opportunities" to prepare societies that will inevitably become more reliant on digital innovation touching all aspects of life.
"As more developers adopt these tools and become fluent in the skill set of prompting with generative AI, it is clear that this new way of software development has created an inextricable link between humankind and artificial intelligence that could well define how the world's software is built for generations to come," the researchers said.
The report, "Sea Change in Software Development: Economic and Productivity Analysis of the AI-Powered Developer Lifecycle," appeared June 26 on the preprint server arXiv.
More information: Thomas Dohmke et al, Sea Change in Software Development: Economic and Productivity Analysis of the AI-Powered Developer Lifecycle, arXiv (2023). DOI: 10.48550/arxiv.2306.15033
Journal information: arXiv
© 2023 Science X Network