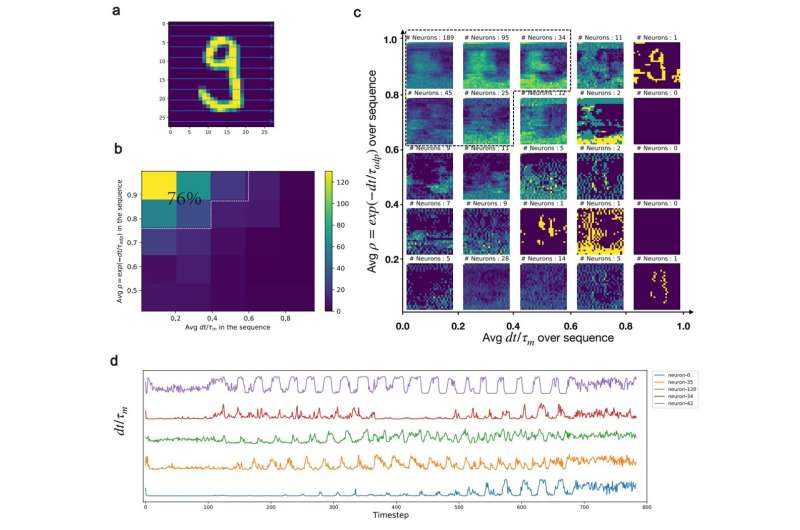
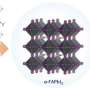
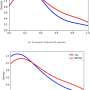
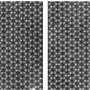
Dynamic neural responses of LTC-SNs. (a) an MNIST sample is sequentially fed into the LTC-SNN, pixel-by-pixel along the row-direction. (b) for illustration, we calculated the histograms of the resulting average dt/t values after training for this single sample (c) average responses of neurons in terms of firing rate binned by dt/tm, exp(dt/tad p) values (d) Example of dynamics of inverse time constant dt/tm for four randomly selected neurons during presentation of the sequence. Credit: Nature Machine Intelligence (2023). DOI: 10.1038/s42256-023-00650-4
In a new study in Nature Machine Intelligence, researchers Bojian Yin and Sander Bohté from the HBP partner Dutch National Research Institute for Mathematics and Computer Science (CWI) demonstrate a significant step towards artificial intelligence that can be used in local devices like smartphones and in VR-like applications, while protecting privacy.
They show how brain-like neurons combined with novel learning methods enable training fast and energy-efficient spiking neural networks on a large scale. Potential applications range from wearable AI to speech recognition and Augmented Reality.
While modern artificial neural networks are the backbone of the current AI revolution, they are only loosely inspired by networks of real, biological neurons such as our brain. The brain however is a much larger network, much more energy-efficient, and can respond ultra-fast when triggered by external events. Spiking neural networks are special types of neural networks that more closely mimic the working of biological neurons: the neurons of our nervous system communicate by exchanging electrical pulses, and they do so only sparingly.
Implemented in chips, called neuromorphic hardware, such spiking neural networks hold the promise of bringing AI programs closer to users—on their own devices. These local solutions are good for privacy, robustness and responsiveness. Applications range from speech recognition in toys and appliances, health care monitoring and drone navigation to local surveillance.
Just like standard artificial neural networks, spiking neural networks need to be trained to perform such tasks well. However, the way in which such networks communicate poses serious challenges. "The algorithms needed for this require a lot of computer memory, allowing us to only train small network models mostly for smaller tasks. This holds back many practical AI applications so far," says Sander Bohté of CWI's Machine Learning group. In the Human Brain Project, he works on architectures and learning methods for hierarchical cognitive processing.
Mimicking the learning brain
The learning aspect of these algorithms is a big challenge, and they cannot match the learning ability of our brain. The brain can easily learn immediately from new experiences, by changing connections, or even by making new ones. The brain also needs far fewer examples to learn something and it works more energy-efficiently. "We wanted to develop something closer to the way our brain learns," says Bojian Yin.
Yin explains how this works: if you make a mistake during a driving lesson, you learn from it immediately. You correct your behavior right away and not an hour later. "You learn, as it were, while taking in the new information. We wanted to mimic that by giving each neuron of the neural network a bit of information that is constantly updated. That way, the network learns how the information changes and doesn't have to remember all the previous information. This is the big difference from current networks, which have to work with all the previous changes. The current way of learning requires enormous computing power and thus a lot of memory and energy."
6 million neurons
The new online learning algorithm makes it possible to learn directly from the data, enabling much larger spiking neural networks. Together with researchers from TU Eindhoven and research partner Holst Center, Bohté and Yin demonstrated this in a system designed for recognizing and locating objects. Yin shows a video of a busy street in Amsterdam: the underlying spiking neural network, SPYv4, has been trained in such a way that it can distinguish cyclists, pedestrians and cars and indicate exactly where they are.
"Previously, we could train neural networks with up to 10,000 neurons; now, we can do the same quite easily for networks with more than 6 million neurons," says Bohté. "With this, we can train highly capable spiking neural networks like our SPYv4."
And where does it all lead? With access to such powerful AI solutions based on spiking neural networks, chips are being developed that can run these AI programs at very low power and will ultimately show up in many smart devices, like hearing-aids and augmented or virtual reality glasses.
More information: Bojian Yin, Accurate online training of dynamical spiking neural networks through Forward Propagation Through Time, Nature Machine Intelligence (2023). DOI: 10.1038/s42256-023-00650-4. www.nature.com/articles/s42256-023-00650-4
Journal information: Nature Machine Intelligence
Provided by Human Brain Project